A research team at Rice University led by James Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor of Chemistry and professor of materials science and nanoengineering, is tackling the environmental issue of efficiently recycling lithium ion batteries amid their increasing use.
The team has pioneered a new method to extract purified active materials from battery waste as detailed in the journal Nature Communications on July 24. Their findings have the potential to facilitate the effective separation and recycling of valuable battery materials at a minimal fee, contributing to a greener production of electric vehicles (EVs).
"With the surge in battery use, particularly in EVs, the need for developing sustainable recycling methods is pressing," Tour said.
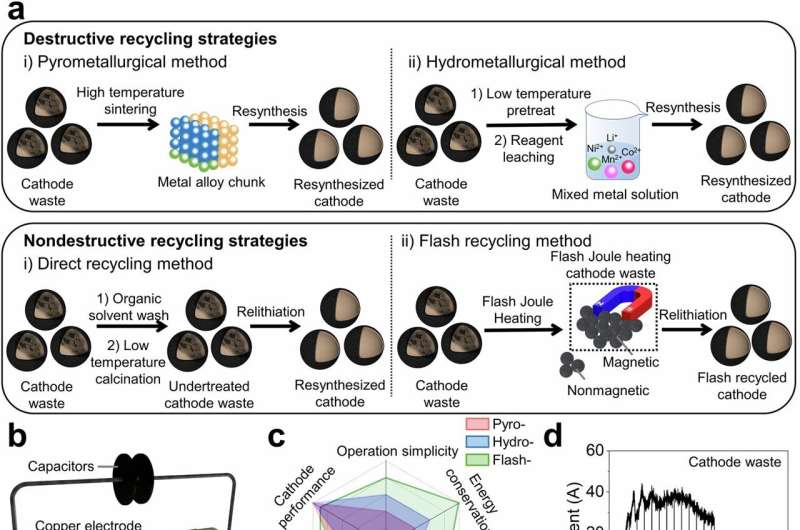
Conventional recycling techniques typically involve breaking down battery materials into their elemental forms through energy-intensive thermal or chemical processes that are costly and have significant environmental impacts.
The team proposed that magnetic properties could facilitate the separation and purification of spent battery materials.
Their innovation uses a method known as solvent-free flash Joule heating (FJH). This technique devised by Tour involves passing a current through a moderately resistive material to rapidly heat and transform it into other substances.
Using FJH, the researchers heated battery waste to 2,500 Kelvin within seconds, creating unique features with magnetic shells and stable core structures. The magnetic separation allowed for efficient purification.
During the process, the cobalt-based battery cathodes—typically used in EVs and associated with high financial, environmental and social costs—unexpectedly showed magnetism in the outer spinel cobalt oxide layers, allowing for easy separation.
The researchers' approach resulted in a high battery metal recovery yield of 98% with the value of battery structure maintained.
"Notably, the metal impurities were significantly reduced after separation while preserving the structure and functionality of the materials," Tour said. "The bulk structure of battery materials remains stable and is ready to be reconstituted into new cathodes."
Rice graduate students Weiyin Chen and Jinhang Chen as well as postdoctoral researcher and Rice Academy Junior Fellow Yi Cheng are the co-lead authors of the study.
More information: Weiyin Chen et al, Nondestructive flash cathode recycling, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50324-x
Citation: Nondestructive flash cathode recycling method uses magnetic properties for battery recycling (2024, July 24) retrieved 24 July 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-07-nondestructive-cathode-recycling-method-magnetic.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
