Researchers have found a way to bind engineered skin tissue to the complex forms of humanoid robots. This brings with it potential benefits to robotic platforms such as increased mobility, self-healing abilities, embedded sensing capabilities and an increasingly lifelike appearance.
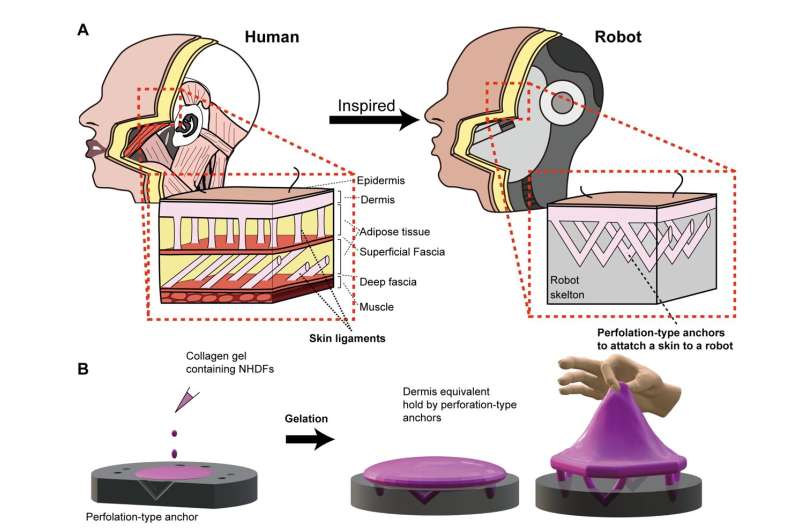
Taking inspiration from human skin ligaments, the team, led by Professor Shoji Takeuchi of the University of Tokyo, included special perforations in a robot face, which helped a layer of skin take hold. Their research could be useful in the cosmetics industry and to help train plastic surgeons. The work is published in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science.
Takeuchi is a pioneer in the field of biohybrid robotics, where biology and mechanical engineering meet. So far, his lab, the Biohybrid Systems Laboratory, has created mini robots that walk using biological muscle tissue, 3D printed lab-grown meat, engineered skin that can heal, and more. It was during research on the last of these items that Takeuchi felt the need to take the idea of robotic skin further to improve its properties and capabilities.
"During previous research on a finger-shaped robot covered in engineered skin tissue we grew in our lab, I felt the need for better adhesion between the robotic features and the subcutaneous structure of the skin," said Takeuchi.
"By mimicking human skin-ligament structures and by using specially made V-shaped perforations in solid materials, we found a way to bind skin to complex structures. The natural flexibility of the skin and the strong method of adhesion mean the skin can move with the mechanical components of the robot without tearing or peeling away."
Previous methods to attach skin tissue to solid surfaces involved things like mini anchors or hooks, but these limited the kinds of surfaces that could receive skin coatings and could cause damage during motion. By carefully engineering small perforations instead, essentially any shape of surface can have skin applied to it.
The trick the team employed was to use a special collagen gel for adhesion, which is naturally viscous so difficult to feed into the minuscule perforations. But using a common technique for plastic adhesion called plasma treatment, they managed to coax the collagen into the fine structures of the perforations while also holding the skin close to the surface in question.
"Manipulating soft, wet biological tissues during the development process is much harder than people outside the field might think. For instance, if sterility is not maintained, bacteria can enter and the tissue will die," said Takeuchi.
More information: M. Kawai, M. Nie, H. Oda, S. Takeuchi. Perforation-type anchors inspired by skin ligament for robotic face covered with living skin, Cell Reports Physical Science (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2024.102066. www.cell.com/cell-reports-phys … 2666-3864(24)00335-7
Citation: Engineered skin tissue grants robots special properties and abilities (2024, June 25) retrieved 25 June 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-06-skin-tissue-grants-robots-special.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
