While the rise of artificial intelligence is proving to be a contentious issue, new research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has found that the use of social robots in a commercial setting would likely be met with less resistance.
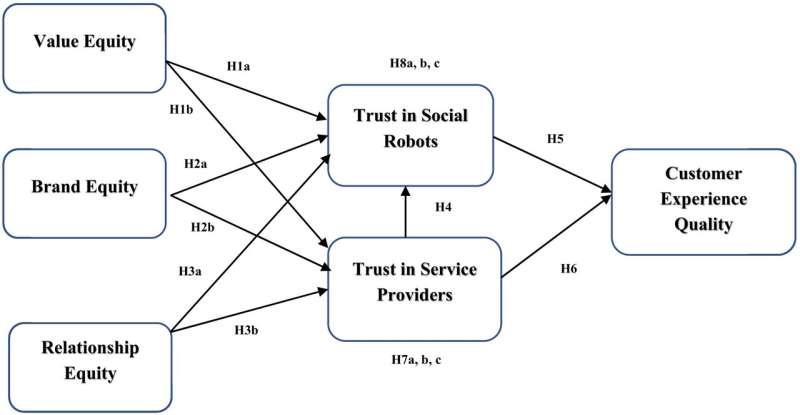
The study, by ECU's Marketing and Service Science Professor Sanjit Roy, investigated the relationships among customer equity drivers such as value equity, brand equity, and relationship equity, trust in social robots, and trust in service providers. The research is published in the journal Technological Forecasting and Social Change.
Professor Roy noted that the increasing prevalence of social robots in retail is consistent with Industry 5.0 tenets, which advocate for "humans and machines acting synergistically."
"The basic idea here is simple: Technology should augment, not substitute, those working in the services industry with flow-on benefits for customers. Indeed, social robots have been shown to act as entertainers, social enablers, friends, and mentors to customers, which suggests that robots can be perceived as supportive, emotional, and hence social actors," explained Roy.
Roy pointed out that social robots could perform many functions and roles with transformative potential when orchestrating customer experiences.
"For example, social robots have proven effective in handling repetitive tasks, like transporting objects and the execution of monotonous assembly jobs. More recently, they have shown that they can perform complex physical and cognitive assignments, such as identifying signs of worsening dementia in patients.
"Additionally, social robots are finding increasingly advanced applications in professional domains such as assisting in financial auditing and even aiding in surgical procedures through voice-activated robotic arms. These advancements enable service providers to scale their offerings, enhance their productivity, reduce operational expenses, and automate service processes, among other benefits," added Roy.
The research has shown that businesses could also benefit from the use of social robots, with effective and efficient customer service creating value equity for a company.
"The presence of social robots for service delivery results in greater perceptions of service quality in terms of efficiency and effectiveness, thereby increasing customers' perceived value equity," Roy said. "The value provided by social robots invokes trust between customers and social robots. Therefore, investing in value equity generates more trust, which can change customers' dispositions towards and interaction with service providers.
"In human-robot interactions, a successful interaction acts as the foundation of a (long-term) relationship, with every subsequent successful interaction generating greater trust between the parties. A series of flawless transactions ultimately leads to a situation or a state of inertia where customers look forward to interacting with the social robots. This implies that investing in relationship equity can generate more trust in social robots. Thus, it is anticipated that relationship equity will influence trust in service providers and trust in social robots."
More information: Sanjit K. Roy et al, Customer experience quality with social robots: Does trust matter?, Technological Forecasting and Social Change (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.techfore.2023.123032
Citation: Businesses can benefit from social robots if trust is established, finds study (2024, February 26) retrieved 26 February 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-02-businesses-benefit-social-robots.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
