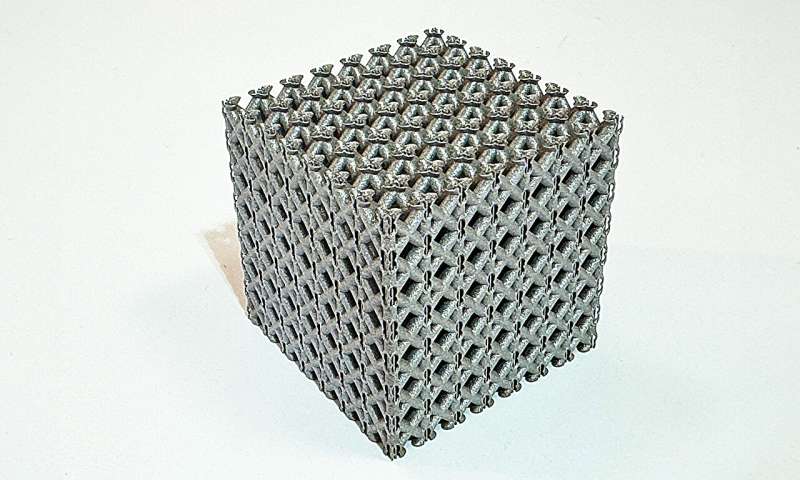
A 3D printed 'metamaterial' boasting levels of strength for weight not normally seen in nature or manufacturing could change how we make everything from medical implants to aircraft or rocket parts.
RMIT University researchers created the new metamaterial—a term used to describe an artificial material with unique properties not observed in nature—from common titanium alloy.
But it's the material's unique lattice structure design, recently revealed in the journal Advanced Materials, that makes it anything but common: tests show it's 50% stronger than the next strongest alloy of similar density used in aerospace applications.
Improving on nature's own design
Lattice structures made of hollow struts were originally inspired by nature: strong hollow-stemmed plants like the Victoria water lily or the hardy organ pipe coral (Tubipora musica) showed us the way to combine lightness and strength.
However, as RMIT's Distinguished Professor Ma Qian explains, decades of trying to replicate these hollow 'cellular structures' in metals have been frustrated by the common issues of manufacturability and load stress concentrating on the inside areas of the hollow struts, leading to premature failures.
"Ideally, the stress in all complex cellular materials should be evenly spread," Qian explained.
"However, for most topologies, it is common for less than half of the material to mainly bear the compressive load, while the larger volume of material is structurally insignificant."
Metal 3D printing provides unprecedented, innovative solutions to these issues.

By pushing the 3D printing design to its limits, the RMIT team optimized a new type of lattice structure to distribute the stress more evenly, enhancing its strength or structural efficiency.
"We designed a hollow tubular lattice structure that has a thin band running inside it. These two elements together show strength and lightness never before seen together in nature," said Qian.
"By effectively merging two complementary lattice structures to distribute stress evenly, we avoid the weak points where stress normally concentrates."
Laser-powered strength
The team 3D printed this design at RMIT's Advanced Manufacturing Precinct using a process called laser powder bed fusion, where layers of metal powder are melted into place using a high-powered laser beam.
Testing showed the printed design—a titanium lattice cube—was 50% stronger than cast magnesium alloy WE54, the strongest alloy of similar density used in aerospace applications. The new structure had effectively halved the amount of stress concentrated on the lattice's infamous weak points.
The double lattice design also means any cracks are deflected along the structure, further enhancing the toughness.
Study lead author and RMIT Ph.D. candidate Jordan Noronha said they could make this structure at the scale of several millimeters or several meters in size using different types of printers.
This printability, along with its strength, biocompatibility, corrosion, and heat resistance, makes it a promising candidate for many applications, from medical devices such as bone implants to aircraft or rocket parts.
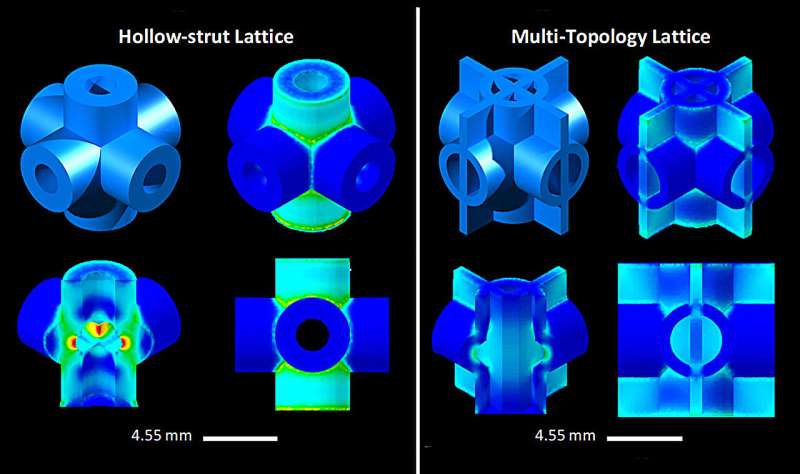
"Compared with the strongest available cast magnesium alloy currently used in commercial applications requiring high strength and lightweight, our titanium metamaterial with a comparable density was shown to be much stronger or less susceptible to permanent shape change under compressive loading, not to mention more feasible to manufacture," Noronha said.
The team plans to further refine the material for maximum efficiency and explore applications in higher-temperature environments.
More information: Jordan Noronha et al, Titanium Multi‐Topology Metamaterials with Exceptional Strength, Advanced Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202308715
Citation: 3D printed titanium structure shows supernatural strength (2024, February 26) retrieved 26 February 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-02-3d-titanium-supernatural-strength.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
