Concrete is an essential material in the construction industry, where it is fundamental to the foundations and structures of dwellings and office buildings, as well as roads, dams and bridges, among many other infrastructure projects. However, the service life of concrete is limited, and it must be monitored in order to guarantee the safety of these structures.
To facilitate fast, low-cost, in-situ analysis that dispenses with the need to take samples to a laboratory, researchers at the University of São Paulo's Physics Institute (IF-USP) in Brazil, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Leuven in Belgium, have developed a luminescent material that reveals the presence of compounds indicating deterioration of concrete when exposed to ultraviolet light.
The results are reported in an article published in Chemical Communications and featured on the front cover of the journal.
Concrete structures last about 50 years on average. Constant absorption of water, salts and gases from the atmosphere causes acidification, leading to corrosion of the steel reinforcing bars (rebars) in slabs, columns and other structural elements, and drastically reducing their weight-bearing capacity.
The lifetime of concrete can be extended through preventive measures such as the addition of protective layers that hinder penetration of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the exposed surfaces of structures. If this intervention is to be timely, the ability to verify and characterize the degree of deterioration is vital.
The main challenge facing engineers who inspect the state of the concrete in buildings and other structures is that drilling to remove samples and their analysis in a laboratory is labor-intensive and costly, as well as being complex in places that are hard to access. It can also be hazardous, since the drilling can cause alterations in the structure and further weaken the concrete if it is already degraded, especially if the procedure is not carried out correctly.
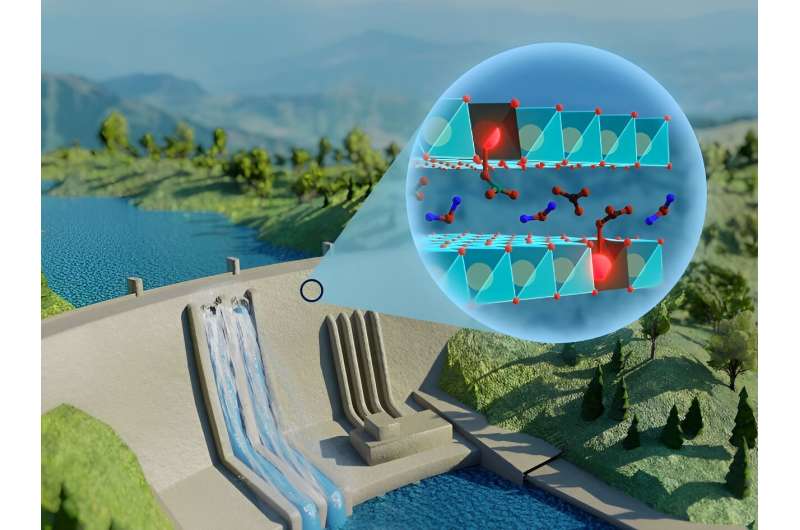
In this study, researchers at IF-USP's Nanomaterials and Applications Laboratory (LNA) developed a catalyst based on layered double hydroxide (LDH), also known as anionic clay, to measure the degree of deterioration in concrete. They added trivalent europium (Eu3+) to produce orange-to-red luminescence.
Laboratory tests showed that when the material was exposed to ultraviolet light (UV), its luminescence changed color according to the amount of carbonate it had absorbed. This effect can be used to detect deterioration in concrete: the greater the redshift, the larger the amount of carbonate and the more degraded the concrete.
"The main advance is that the material can help determine in real time how the concrete present in a structure is deteriorating and when the structure will require maintenance, without any need for drilling or waiting for laboratory analysis. This contributes to more agile decision-making, facilitates preventive maintenance, and helps avoid accidents that can cost lives and cause considerable economic damage," said Alysson Ferreira Morais, first author of the article.
According to the scientists, the next step will entail developing a sensor that detects the luminescent material and testing it under real-world conditions to verify specific factors such as weatherability and stability inside concrete.
Safety, cost and carbon footprint
In addition to its contribution to building safety, the new method offers potential benefits in terms of two other highly important aspects of present-day economies: costs, and carbon reduction.
"The longer buildings last, the less need to invest in new structures, and the more the construction industry contributes to the effort to cut greenhouse gas emissions, 8% of which come from the industry globally, owing to production of concrete and construction itself," said Danilo Mustafa, last author of the article and a professor at IF-USP.
Researchers at the University of Kiel in Germany also took part in the study.
More information: Alysson F. Morais et al, Eu3+ doped ZnAl layered double hydroxides as calibrationless, fluorescent sensors for carbonate, Chemical Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D3CC03066K
Citation: Novel material facilitates measurement of concrete deterioration in buildings and other structures (2024, January 23) retrieved 23 January 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-01-material-concrete-deterioration.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
