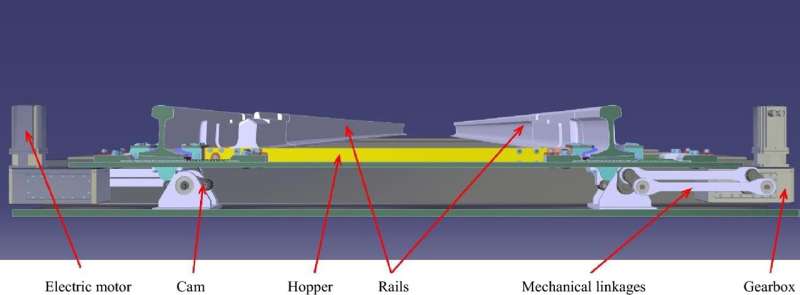
Researchers from the University of Birmingham, U.K., are working on Repoint, a new cutting-edge railway switch (points) technology to improve upon the traditional design, which has been in use for over 200 years.
While conventional railway switches guide trains from one track to another by sliding a pair of tapering rails horizontally, the new design, which is called Repoint, uses a lift and move mechanism, which includes a passive lock for when the points are in place. This is combined with a stub-switch type layout, which offers advantages in many situations. Importantly, the switch is "fault-tolerant," continuing to work even when two of the three actuators, which control the movement of the points, have failed.
Research published in Railway Engineering Science by the team (now at University of Birmingham, Leeds, Loughborough, and Network Rail) describes the team's development of a digital twin (dynamic simulation model) which has been used to show that the design meets and exceeds requirements for speed and performance.
The research investigated the performance of the switch using a novel method for simulating track system behavior, which combines rail bending with physics-based models of actuators and control systems. The simulation scenarios included one of power failure to four of the six motors that drive the actuators, and showed that a single actuator is capable lifting and moving the points to the desired position.
Repoint was developed by Professor Roger Dixon, who led a team at Loughborough University until 2018, and is now Professor of Control Systems Engineering at the Birmingham Center for Railway Research and Education (BRCCE).
The journey to a new railway switch started when Roger, then Head of Loughborough's Control Systems Research Group, responded to a joint call from the Engineering and Physics Research Council (EPSRC) and the UK Rail Safety and Standards Board (RSSB) to look at ways of improving capacity on existing lines.
It was clear that one significant limiting factor to growing capacity was the railway track switch, and so a project to re-imagine the switch was proposed and subsequently funded (having ranked 1st in the peer review for the call).
Professor Dixon commented, "Although switches account for less than 5% of railway track miles, they contribute to 18% of delay minutes, and 17.5% of delay costs in the UK."
The team engaged with operators, maintainers and designers to understand the limits and issues with existing switch technology.
One of the most significant findings was the "single point of failure" that is embedded in the traditional switches and their detection systems, so the new switch incorporates fault-tolerant design.
Inspired by aircraft control systems, the team designed a switch that remains operational even when two (out of three) components fail.
Professor Dixon said, "While railway networks continue to carry more passengers and freight, building new track is always difficult and expensive, and increasing the reliability and exploiting the capacity of existing routes is generally the preferred option."
Repoint actuation is at Technology Readiness Level (TRL) 4–5. It has been successfully tested at a test track, which demonstrated its compatibility and functionality with conventional switch rail arrangements. The researchers are now seeking partners and funding to design and fully test the full repoint system including the actuators, p-way and interfaces to signaling.
More information: Saikat Dutta et al, A framework for dynamic modelling of railway track switches considering the switch blades, actuators and control systems, Railway Engineering Science (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s40534-023-00324-2
Citation: Novel railway point switching technology, inspired by aircraft control systems (2024, January 10) retrieved 10 January 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-01-railway-technology-aircraft.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
